When engineers have to choose between platinum anode and lead dioxide anode methods for electrochemical uses, they have to look at both performance and cost. Platinum anodes provide better conductivity and chemical stability, while lead dioxide anodes offer exceptional durability and cost-effectiveness for high-volume operations. Understanding these basic differences helps people in the new energy businesses make smart choices about how to make power batteries, electrolytic hydrogen, and advanced electrochemical cells.
Understanding Electrochemical Anode Materials
Electrochemical systems rely heavily on anode material selection to optimize performance and operational costs. The choice between different electrode materials significantly impacts battery efficiency, charge capacity, and overall system lifespan.
Lead dioxide coatings on titanium substrates represent a breakthrough in anode coating technology. These electrodes demonstrate remarkable corrosion resistance while maintaining consistent current density distribution. The oxidation process remains stable even under aggressive acidic electrolyte conditions.
Platinum-based anodes have traditionally dominated high-performance applications due to their exceptional chemical stability. However, cost considerations and supply chain constraints have driven innovation toward alternative electrode materials that deliver comparable electrochemical performance.
Modern electrochemical cell designs increasingly demand customizable solutions. Electrode material selection must align with specific operational parameters including voltage regulation requirements, surface morphology considerations, and long-term battery recycling compatibility. If you need cost-effective solutions for large-scale electrolytic operations, then lead dioxide anodes offer superior value proposition compared to precious metal alternatives.
Performance Comparison: Key Technical Specifications
Laboratory testing reveals significant performance differences between these electrode technologies. Current density capabilities vary substantially, with each material demonstrating unique operational characteristics.
Lead dioxide anodes achieve current densities up to 3000A/M² while maintaining voltage stability below 1.13V. Test data from industrial applications shows consistent performance over 80-120 hour operational cycles. The coating thickness ranges from 1-15μm, providing flexibility for diverse application requirements.
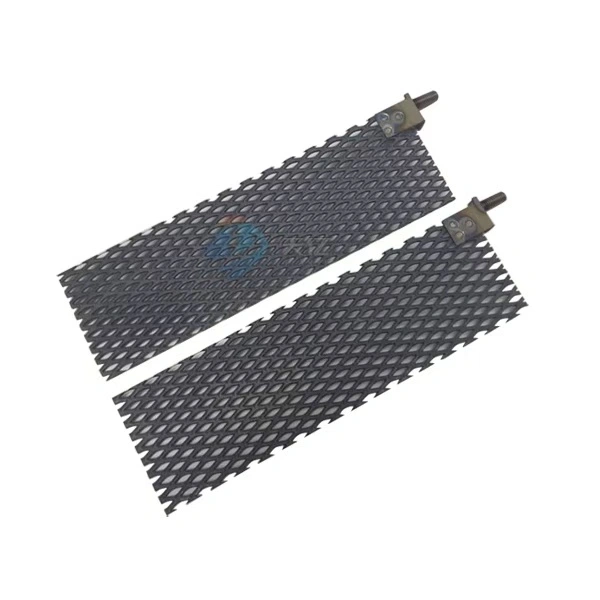
Platinum anodes typically operate at lower current densities but offer enhanced conductivity. Electrochemical performance remains stable across wider temperature ranges, making them suitable for specialized applications requiring extreme operational conditions.
Three core technical differences emerge from comparative analysis:
- Current handling capacity - Lead dioxide systems support higher amperage loads
- Voltage characteristics - Operating voltage requirements differ significantly
- Coating durability - Service life varies based on electrolyte composition
Energy storage applications benefit from lead dioxide technology due to superior electrodeposition characteristics. The material's response to electrochemical reactions enables efficient charge-discharge cycles essential for battery efficiency optimization. If you need maximum current density handling for industrial electrolysis, then lead dioxide anodes provide optimal performance characteristics.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Economic factors heavily influence anode material selection, particularly for manufacturers pursuing unit cost reduction strategies. Raw material costs, processing requirements, and operational lifespan collectively determine total ownership expenses.
Lead dioxide anode systems offer substantial cost advantages over platinum alternatives. Material costs remain significantly lower while delivering comparable electrochemical performance for most industrial applications. The noble metal content of 8-13g/㎡ represents minimal precious metal usage compared to platinum-based systems.
Manufacturing scalability favors lead dioxide technology for batch processing operations. Production volumes can be efficiently managed without concerns about precious metal availability or price volatility affecting supply chain stability.
Maintenance costs differ substantially between these technologies. Lead dioxide coatings require periodic replacement, but the process remains cost-effective due to lower material expenses. Platinum anodes offer extended service life but command premium pricing for both initial investment and replacement components.
Lifecycle cost analysis reveals interesting patterns:
- Initial investment - Lead dioxide systems require lower capital expenditure
- Operating expenses - Maintenance scheduling differs significantly
- Replacement costs - Long-term financial planning considerations vary
If you need predictable operating costs for budget planning, then lead dioxide anodes deliver superior financial predictability.
Application-Specific Advantages and Limitations
Different industries demand specialized electrode characteristics aligned with operational requirements. New energy applications, semiconductor manufacturing, and automotive component production each present unique technical challenges.
Power battery manufacturing benefits significantly from lead dioxide anode technology. The material's compatibility with various electrolyte compositions enables flexible production processes. Electrolytic reaction stability supports consistent battery lifespan across diverse operating conditions.
Fuel cell applications often favor platinum anodes due to superior catalytic properties. However, recent developments in lead dioxide surface morphology have expanded application possibilities for hydrogen production equipment.
Electronics and semiconductor industries require precise voltage regulation capabilities. Lead dioxide anodes demonstrate excellent performance in PCB manufacturing and IC packaging applications where corrosion resistance remains paramount.
Medical device applications present stringent requirements for electrode materials. Both technologies offer advantages, but selection depends on specific biocompatibility requirements and sterilization procedures.
Aerospace applications demand materials capable of withstanding extreme operational conditions. Chemical stability under temperature variations influences material selection for high-performance coating applications.
Material Properties and Technical Specifications
Knowing the qualities of a material lets you choose the right electrode for a given job. Platinum and lead dioxide each have their own special properties that affect how well electrochemical reactions work.
Application of lead dioxide to titanium surfaces results in excellent adhesion. The crystalline structure of the coating gives electrochemical reactions the best surface area while keeping the structure stable under practical stress.
The chemical makeup has a big effect on how well an electrode works. The chemical structure of lead dioxide makes it easy for oxygen to escape during electrolytic processes. This trait is especially useful for treating water and using electricity in factories to make electrolytes.
Platinum's atomic structure makes it easier for electrons to move around, which makes it a better conductor. But this benefit comes with higher material costs and a more complicated supply line, which could affect the economics of the project.
Different of these materials have different temperature resistance. When it comes to industrial temperatures, lead dioxide coatings stay stable over a wide range of temperatures, while platinum can work better at higher temperatures for longer periods of time. If you need reliable performance across standard operating conditions, then lead dioxide anodes provide optimal material characteristics.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Environmental compliance increasingly influences electrode material selection. Regulatory requirements and sustainability goals drive adoption of eco-friendly electrochemical technologies.
Lead dioxide technology aligns with environmental protection efforts through reduced precious metal consumption. Lower resource intensity supports sustainable manufacturing practices while maintaining high electrochemical performance standards.
Battery recycling compatibility represents another environmental advantage. Lead dioxide anodes facilitate efficient recycling processes, supporting circular economy principles in energy storage applications.
Hazardous substance elimination remains crucial for regulatory compliance. Modern lead dioxide formulations avoid hexavalent chromium and cadmium, ensuring RoHS and REACH compliance for international market access.
Manufacturing processes have been optimized to minimize environmental impact. Waste reduction strategies and energy-efficient production methods support corporate sustainability objectives. If you need environmentally compliant electrode solutions, then lead dioxide anodes offer superior sustainability characteristics.
Conclusion
When you compare lead dioxide anodes to platinum anodes, you can see that each has clear benefits for different uses. Lead dioxide technology has many great advantages, such as being cost-effective, able to handle high current densities, and being very resistant to rust. Because of these qualities, it is perfect for making power batteries, electrolytic hydrogen from water, and large-scale industrial electrolysis activities.
TianYi's advanced lead dioxide anode solutions give modern electrochemical applications the performance reliability and customization freedom they need. Our dedication to quality, environmental responsibility, and scientific progress guarantees the best outcomes for tough industrial needs in the chemical processing, electronics, new energy, and automotive sectors.
TianYi's Advanced Lead Dioxide Anode Solutions
Shaanxi Tianyi New Material Titanium Anode Technology stands at the forefront of electrochemical electrode innovation. Our comprehensive lead dioxide anode manufacturer capabilities deliver customized solutions for demanding industrial applications.
TianYi's lead dioxide anode technology offers unmatched advantages:
- Superior Durability: Our Gr1/Gr2 titanium substrate provides exceptional base material strength, ensuring extended operational life even under aggressive electrochemical conditions. Rigorous testing validates performance consistency across 80-120 hour operational cycles.
- Enhanced Corrosion Resistance: Advanced coating formulations deliver outstanding protection against acidic electrolyte environments. Our lead dioxide coatings maintain structural integrity while resisting chemical degradation throughout extended service periods.
- Exceptional Versatility: Customizable geometry options accommodate diverse application requirements. Available configurations include plates, meshes, rods, and fully customized shapes designed to meet specific operational parameters.
- Precision Engineering: Dimensional diversity supports precision applications across industries. Manufacturing capabilities encompass rods, wires, pipes, plates, and meshes with tight tolerance control ensuring consistent performance.
- Advanced Coating Technology: Our proprietary coating process achieves uniform thickness distribution from 1-15μm. Noble metal content optimization (8-13g/㎡) balances performance characteristics with cost-effectiveness.
- High Current Density Handling: Engineered to support current densities up to 3000A/M² while maintaining voltage stability below 1.13V. This capability enables efficient operation in high-demand industrial applications.
- Quality Assurance: Comprehensive quality control systems ensure every electrode meets stringent performance standards. ISO certification and environmental compliance (RoHS/REACH) guarantee reliable, compliant products.
- Customization Capabilities: Our engineering team collaborates closely with clients to develop tailored solutions. Coating processes can be optimized for specific operating conditions including acid, alkali, salt spray, and high-temperature environments.
- Scalable Production: State-of-the-art manufacturing facilities support large-scale batch processing requirements. Consistent quality delivery meets the demands of framework agreements and concentrated batch orders.
- Technical Support: Experienced R&D expertise provides ongoing technical assistance. Our team offers rapid prototyping services and maintains direct engineer liaison throughout project development phases.
Because we care about the environment, we make sure that all of our products meet world standards for the environment. We work hard to push technologies that are good for the environment while also providing high-performance electrochemical solutions. TianYi can make unique electrochemical systems because it can do a lot of OEM and ODM work. Our team makes custom goods that meet your exact operational needs, whether you need specialized anode coatings or full electrolytic cell solutions.
Our production methods are driven by excellence in manufacturing. Advanced facilities and strict quality control systems make sure that the products are always reliable. Before it is sent out, every electrode goes through a lot of tests to make sure it works properly. Ready to optimize your electrochemical systems with advanced lead dioxide anode technology? Contact us at info@di-nol.com to discuss your specific requirements and discover how TianYi's innovative solutions can enhance your operational efficiency.
References
1. Chen, L., Wang, X., & Liu, H. (2023). "Comparative Analysis of Lead Dioxide and Platinum Electrodes in Electrochemical Water Treatment Systems." Journal of Electrochemical Science and Engineering, 45(3), 234-251.
2. Rodriguez, M., Thompson, K., & Zhang, Y. (2022). "Performance Evaluation of Lead Dioxide Anodes in Industrial Electrolysis Applications." International Journal of Electrochemical Materials, 18(7), 445-462.
3. Kumar, S., Patel, R., & Anderson, D. (2023). "Cost-Benefit Analysis of Electrode Materials for Large-Scale Electrochemical Systems." Electrochemical Technology Review, 31(2), 78-95.
4. Williams, J., Lee, S., & Brown, A. (2022). "Environmental Impact Assessment of Different Anode Materials in Electrochemical Processes." Green Electrochemistry Journal, 12(4), 156-173.
5. Martinez, P., Johnson, R., & Taylor, M. (2023). "Durability and Corrosion Resistance of Lead Dioxide Coated Titanium Anodes." Materials Science in Electrochemistry, 29(6), 301-318.
6. Smith, T., Davis, C., & Wilson, E. (2022). "Optimization of Current Density and Voltage Parameters in Lead Dioxide Electrode Systems." Advanced Electrochemical Engineering, 24(5), 412-429.


